Ericsson: ‘Network slicing is the operators’ best answer on how to build and manage a network that meets and exceeds the emerging requirements from a wide range of users’
5G network slicing is a feature of a cloud-native 5G network architecture that leverages the principles behind network functions virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN), allowing for flexible, programmable converged networks wherein disparate services that would typically require parallel systems reside on a single infrastructure. In such an architecture, each network “slice” is an isolated, bespoke end-to-end network tailored to fulfill the requirements of a particular application.
Or you can take Ericsson’s definition: “Network slicing is the operators’ best answer on how to build and manage a network that meets and exceeds the emerging requirements from a wide range of users.”
With network slicing, various services based on the requirements of the user and use cases can be offered on a single network. For example, as Samsung explained when announcing a partnership with KDDI, a hospital can use network slicing on its network to prioritize different performance needs, such prioritizing more bandwidth to emergency room admissions, and less to visitor services, which are lower priority.
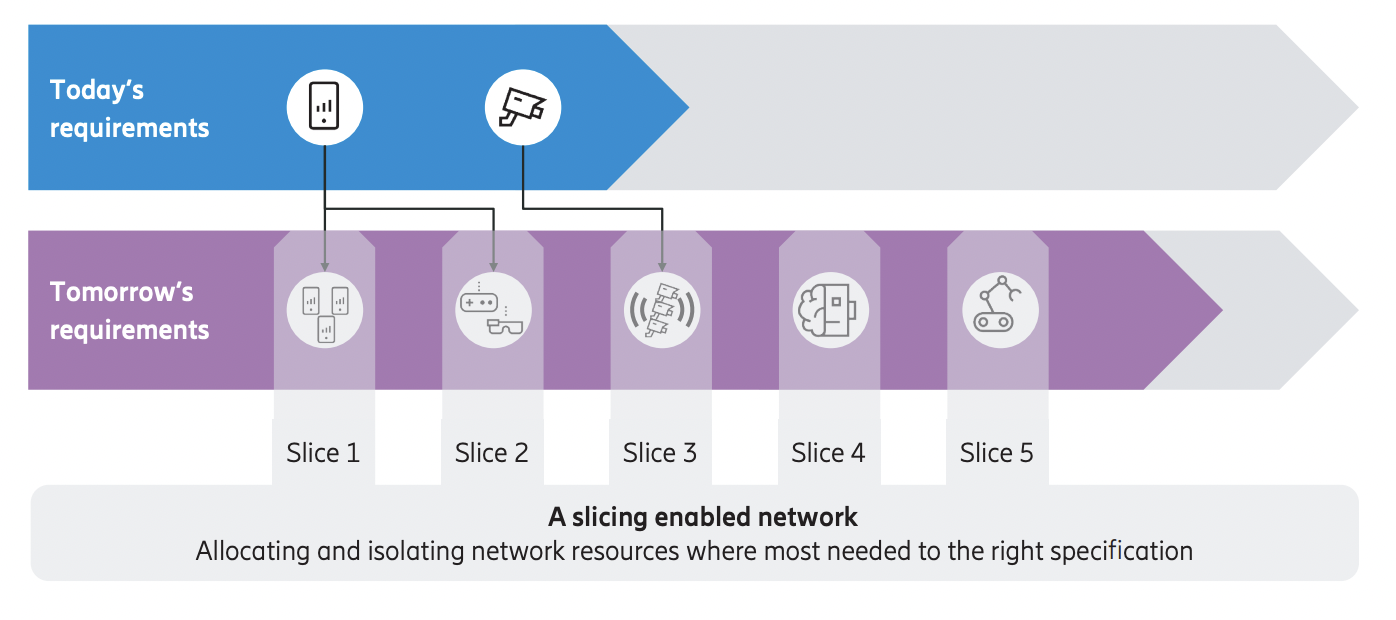
Some of the most salient benefits of the technology include increased efficiency due to the ability for network operators to allocate the needed resources per network slice, the reduction of network operators’ operating expenses (OpEx) and capital expenses (CapEx) and the improvement of operational efficiency and time to market for the delivery of 5G network services.
While network slicing implementations on 4G networks have been announced, network slicing, when used in tandem with 5G networks, will be a critical driver of enterprise 5G adoption. Applications that are enabled or enhanced by the latest generation of cellular technology need greater bandwidth, more connections and lower latency, making network slicing more necessary and all around more desirable.
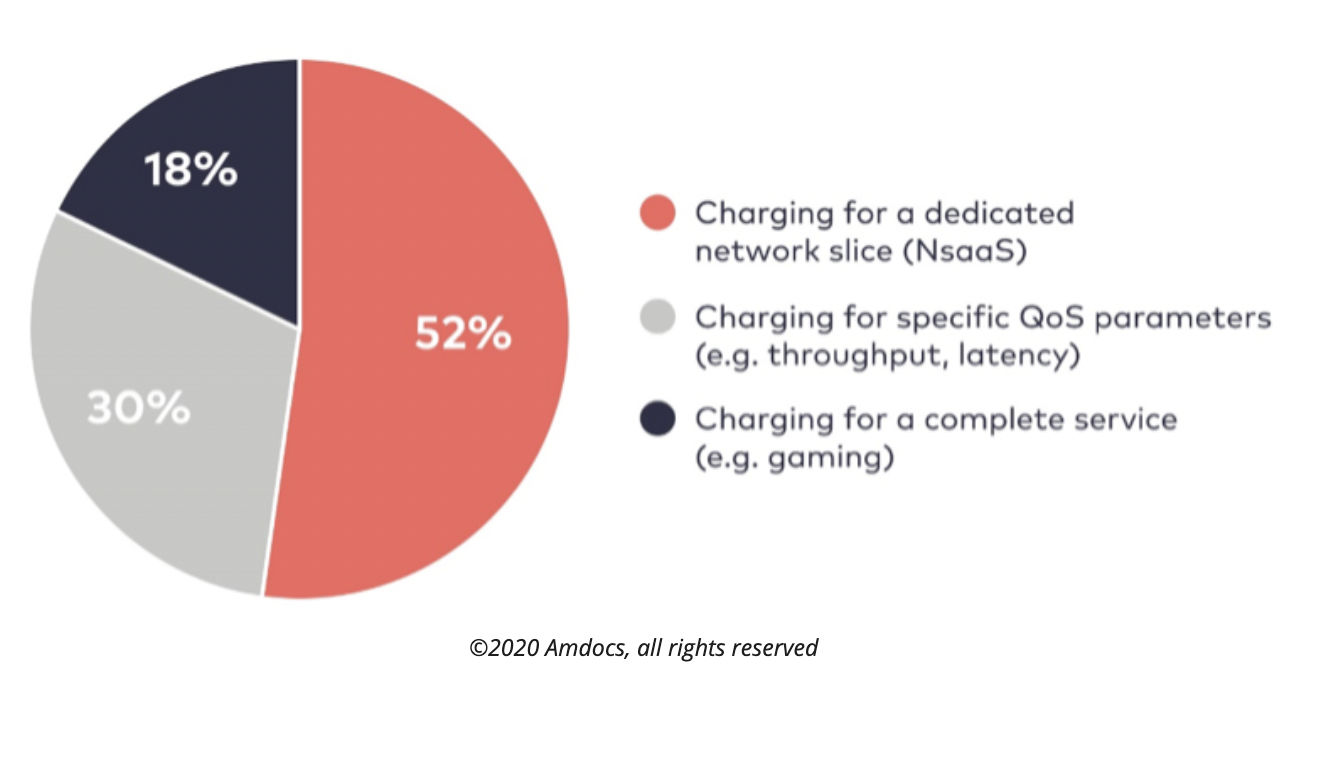
5G network slicing will also make it possible for carriers to offer new services and business models for their enterprise customers. According to a 2020 Amdocs-led survey of 50 mobile operators across the globe, 52% believe Network Slice as a Service (NSaaS) will be the leading approach to network slice monetization, while 30% expect to charge for specific QoS parameters (e.g. throughput, latency).
For the most part, fully fledged dynamic network slicing is still in development, but 5G networks are quickly coming online and expanding, putting the pressure on operators to pilot network slicing and to decide how best to capitalize on this capability.
The post What is 5G network slicing and what does it mean for enterprise 5G adoption? appeared first on RCR Wireless News.
