Open RAN, the movement in wireless telecommunications to disaggregate hardware and software, to open interfaces and reduce costs is taking off. With Open RAN and the “virtualization” it brings, operators are enabled to run software-based network functions on standard commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) servers. With non-proprietary, open interfaces MNOs can use one supplier’s radios with another’s servers, etc. – something not previously possible. As Open RAN architecture expands and becomes commonplace, components and technology continue to advance. The following are our predictions for 2022 and beyond with respect to technology:
1) The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) Continues to Advance – Enabling Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) as it sounds, provides the brains and intelligence for the Open RAN network. Such architecture enables unprecedented means for controlling radio resources in comprehensive ways. The RAN Intelligent Controller known as the RIC is a suite of Software Apps to enable Software Defined Network (SDN) functionalities in Open RAN networks.
There are two types of RICs, the near real–time RIC (near-RT RIC): Provides programmatic control of open centralized units (O-CUs) and open distributed units (O-DUs) on time cycles of 10ms to 1 second.
The non–real–time RIC (non–RT RIC): Provides higher layer policies that can be implemented in the RAN either via the near-RT RIC or via a direct connection to RAN nodes.
As the RIC continues to evolve and mature it will enable Open RAN solutions that can apply data science leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies to significantly improve performance, and enable operation automation, through algorithms that learn from experience and continuously improve the system.
2) Open RAN Networks Enabling 5G with Standalone Core Takes Off
The ultrafast speeds of 5G, high bandwidth and low latency are opening a plethora of new opportunities and advanced applications, transforming industries from manufacturing and healthcare, to Internet of Things (IoT), virtual reality, and gaming, the possibilities are endless.
According to the Competitive Carriers Association (CCA), the U.S. Government and industry stakeholders are focused on the critical need to ensure rapid 5G deployments nationwide. Research and modeling from several economists and firms align to detail the massive impact 5G will have on our economy and job creation, including contributing as much as $1.5 trillion to U.S. GDP and creating 4.5 million jobs.
Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) have two ways of supporting 5G. The Non-standalone standard utilizes existing LTE RAN and core networks as an anchor, with the addition of a 5G component carrier. Non-Standalone will lock MNOs in with their existing vendors as the interfaces are not open and interoperable.
5G Standalone (SA) uses cloud-based and Service-Based Architecture (SBA) that optimizes network infrastructure with virtualized network functions (VNFs), enabling operators to launch differentiated services, ensuring a higher quality of service. 5G SA Open RAN networks are ideal for new applications and will be deployed more and more in 2022 and beyond as they provide ultra-reliable, lower-latency communications, allowing more people and devices to use mobile data at the same time, thus enabling true 5G connectivity.
3) Software Solutions Accelerate the Evolution of the RAN
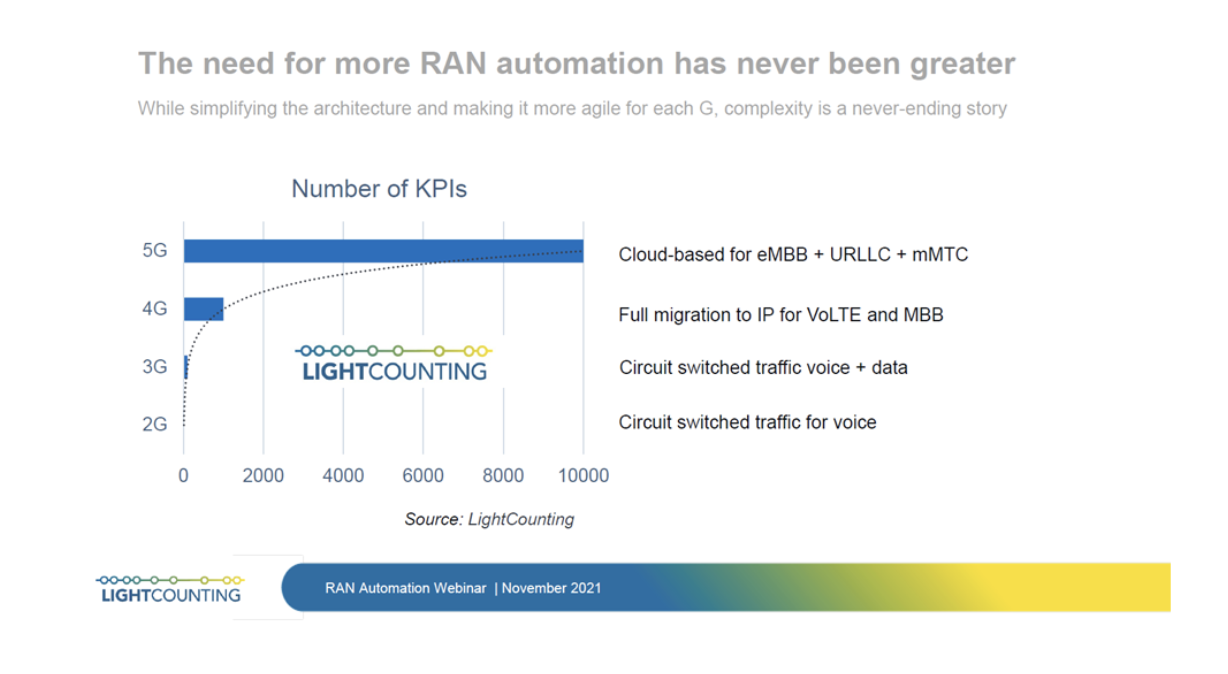
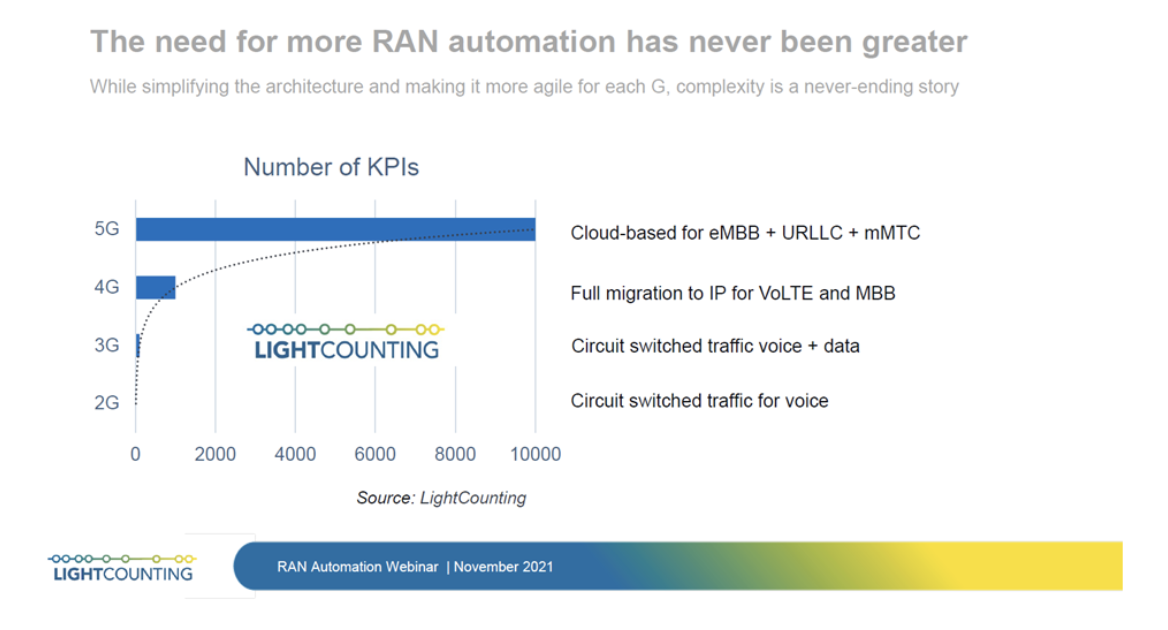
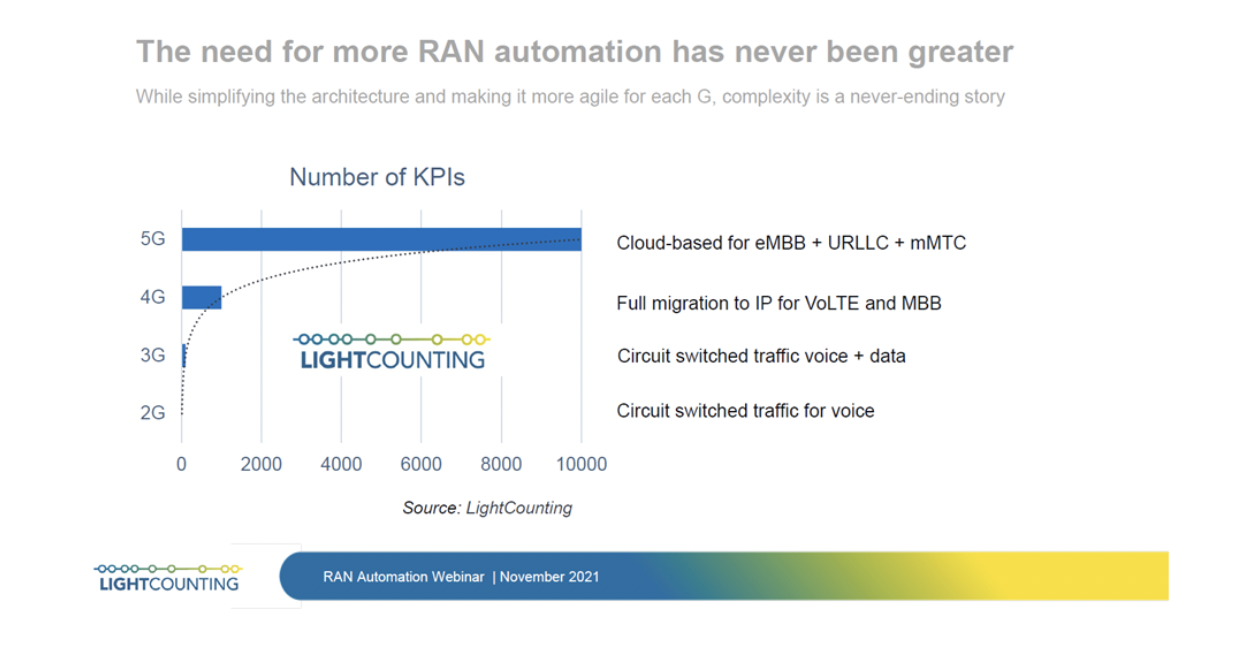
The O-RAN Alliance publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members with integration and testing of their implementations. The O-RAN Software initiatives are focused on aligning a software reference implementation with the O-RAN Alliance’s open architecture and specifications. The aim is to create software solutions that can unify and accelerate the evolution and deployment of the RAN. According to LightCounting Market Research the need for RAN software and automation is continuing to grow including the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and Service Management & Orchestration (SMO) ecosystems.
The key elements of the O-RAN Alliance’s architecture include:
- Service Management and Orchestration Framework (SMO) – is responsible for the management and orchestration of the managed elements under its span of control. The framework can for example be a third-party Network Management System (NMS) or orchestration platform.
RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) – is a software-defined component of the Open Radio Access Network architecture that’s responsible for controlling and optimizing RAN functions.
O-Cloud – is a cloud computing platform made up of the physical infrastructure nodes using O-RAN architecture. It also creates and hosts the various Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) used by the RICs and other infrastructure elements.
O-RAN Central Unit (O-CU) – performs the high-level packet processing and cyphering type functions.
O-RAN Distributed Unit (O-DU) – performs packet scheduler and MAC layer functions.
O-RAN Radio unit (O-RU) – performs lower layer signal and radio processing and RF functions.
The O-RAN Alliance is driving the next generation RAN to new levels of openness, efficiency, flexibility, and intelligence with a broader ecosystem of software driven components.
Open RAN architecture enabling cost-efficient, agile, wireless networks of today and tomorrow is becoming more commonplace and advances in technology are quickly multiplying. The future is bright for Open RAN networks as technology innovations continue to accelerate, enabling state-of-the-art, intelligent broadband communications which improve lives and enhance economies across the globe.
The post Open RAN adoption accelerates in 2022 and beyond—advances in technology (Reader Forum) appeared first on RCR Wireless News.
