Editor’s note: Click here for part 1 and here for part 2 of this three-part series on blockchain technology in the telecom industry. The first six telecom applications of blockchain are covered in part 2.
Blockchain applications in the telecom industry
7. Blockchain in roaming management
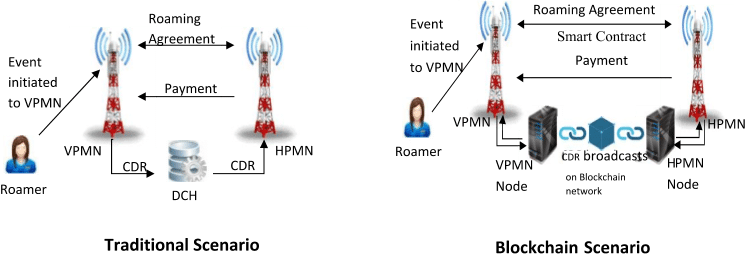
These telco services are provided by their network remotely, while remaining away from home network, via retrieving it through a different network service provider (VPMN). Mobile operators suffer consequential fraud losses due to ever increasing number of International Revenue Share Fraud (IRSF) cases. Often Telcos outsource transmission of C/EDR files and its conversion into billing traffic according to individual’s subscription to the third party, called DCH (Data Clearing House).
The permissioned blockchain can replace the conventional ways of sending C/EDRs. All the communication service providers (CSPs), which have undergone roaming agreement, can broadcast C/EDRs on permissioned blockchain network.
Permissioned nature of blockchain allows only authorized access to the network, so there will be no any chance of data invasion. The Hyperledger blockchain restricts the transfer of unwanted blocks of the blockchain to designated nodes of VPMN and HPMN act as miners to verify the authenticity of the data broadcasted on blockchain network. Whenever a request to start an event is initiated by a roamer, a transaction having all the details about C/EDR data is broadcasted on the network. Since the transfer of communication happens in runtime, the HPMN can calculate billing amount for each and every subscriber, and also the payment to VPMN on runtime itself (in the traditional system, the long time needed by HPMN does not allow a roaming fraud detection before it occurs, there are more technical difficulties for prevention, detection, and automatic response to initiating actions against fraud).
Blockchain can solve the age-old problem to integrate high-cost systems of traditional operators and it provides access/authentication settings for enabling roaming calls across networks and operators.This helps to achieve certified and smooth settlement transition between HPMN and VPMN, without having fear of fraud.
Moreover, in the blockchain scenario, since C/EDRs being transferred through blockchain network via broadcasting, so it makes the role of DCH irrelevant. It helps telecoms to save even more cost as this process does not require a middleman.
Blockchain can enable complex datasets across multiple parties, in real time with high trust and security. Blockchain enables complex datasets across multiple parties and PoCs demonstrated that blockchain can be used to reduce the amount of time needed for inter-carrier voice minute settlements from hundreds of hours to just a few minutes. It involves the implementation of a bilateral blockchain that records and reports transactions to a public blockchain. Smart contracts are used to resolve disputes, settlement transactions, compensations and to rate C/EDRS.
8. Blockchain in support for the internet of things
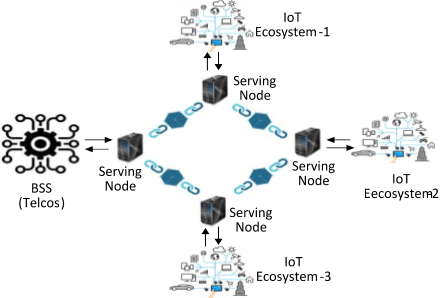
The applications for IoT devices include smart city, smart home, connected car, connected vehicles, smart agriculture, smart entertainment and much more. There is no doubt that this list will grow even further in the near future. Frost & Sullivan forecasts that by 2020, the market for smart cities will reach $1 trillion. It is predicted that by 2020 there will be 200 billion connected devices, which could result in an increased probability of devices being vulnerable to attacks.
Apart Hardware challenges (such as Longevity…), the main items in developing IoT devices are Connectivity, Privacy, Compatibility and Security.
The current ecosystem for IoT is highly centralized and completely relies on the internet for any sort of communication amongst connected devices which makes it highly vulnerable if security is not prioritized. Traditional systems are subject to several points of failure such as Packet loss, Cloud services Interoperability issues, Single point of failure…. etc.
Blockchain provides a secure dynamic peer-to-peer distributed network solution through the utilization of nodes which can be represented by embedded IoT sensors that verify every block being captured into a real-time monitoring system for IoT systems.
With the implementation of blockchain technology in IoT ecosystem, the Centralized model can be replaced by Distributed Digital Ledger (DDL) for all the transactions, makes extremely secure peer-to-peer self-managed network …. which overcomes some of the IOT challenges.
9. Blockchain for money transfer and micro payments
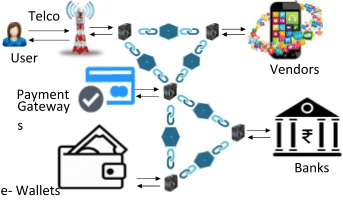
Apart from basic telecommunications services, VAS and OTT services are the two main types of services which consumers get by availing.
- VAS is a non-core service to add value to telcos entire service offerings. They are provided by the operator itself or by an external third-party vendor.
- OTT services are beyond the control or responsibility of telcos. They just carry IP packets from source to destination through their network. The user is free to use OTT services because everyone is independent to use the internet the way they want. Telcos have to integrate VAS and SDP to provide such services to the consumers.
VAS contents or OTT services can be charged and subscriptions can be bundled with telcos’ offers. In all these collaboration models, telcos bill to the consumer usage and pay money back to the VAS or OTT vendors for their proposed content, after keeping their share. IP packets of VAS or OTT services flow as same as the basic services offered on telcos’ network.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is the technology used by telcos to segregate these packets. DPI enables telcos to read & scan the payloads of each packet, unlike only headers in old techniques, in run time so the decision on how to classify & control traffic on their network have been taken based on applications, content, and subscribers also along with origin and destination.
With the implementation of blockchain technology in micro payments network, not only will transactions cost reduce but it will lead to an effective run-time billing and validation processing of any transaction.
Micropayments can have a blockchain network accommodating a recent scalable protocol called ‘Raiden Network’. This protocol can handle over one million transfers per second without running into any problems such as latency (obliging the operators to pay the vendors before billing the consumers), packet losses, inability to handle IP packets efficiently, Interconnect issues, OTT Bypass, and other vulnerability issues of traditional concepts that generate huge revenue leakage for the operators.
For the money transfer aspect, Blockchain has enabled cost-effective international remittances across the globe with very minimal transaction charges. Telecom operators can become global remittance providers.
10. Blockchain for smart transactions and revenue streamlining
Blockchain has enabled purchasing of digital assets, including music, mobile games, gift cards and loyalty points. Similarly, blockchain-based services have started popping up looking to be first to corner the emerging market trends with a superior customer experience.
Some Wireless applications, for instance, offers a service that lets users purchase mobile or sending data directly on their mobile phones.
Other blockchain telecommunications pioneers (Such as Qlink….) are building out its infrastructure to provide tools like wi-fi sharing, mobile data, and enterprise-to-peer services.
Smart contract is one of the features accommodated by blockchain, which has the intrinsic nature and potential to substantially boost efficiency in many areas of business and law.
11. Blockchain in billing
Current systems still have to resolve some main issues due to technical limitations resulting from:
- An improper integration of network elements: Synchronization between HLR and BSS generating leakage of revenues…
- The introduction of new products: Whenever telcos announce a new product, OSS/BSS system along with core network elements need to communicate well about the new price slabs….
- The incomplete usage/consumption information: due to the changing trends in technologies, the data usage load and complexity….
- The scalability issues.
- The processing speed: capacity of processing remaining balance/billing transactions at the evolving speed of the network/internet (i.e.: 5G)
- Revenue leakage vulnerability of the Billing for post-paid customers.
With the blockchain technology:
- In the core network, switches and various registers can be put on blockchain network. It will help the switches to fetch in real-time all the information regarding consumers. The blockchain node of OSS/BSS systems, enabling a perfect synchronization with switch and registers.
- All nodes will work as miner on this blockchain network and when a consumer raises any request to subscribe or unsubscribe from any service, that request will be put on blockchain network by BSS and the nodes of switches and registers will update themselves accordingly through their nodes. Every status updating related to consumer in any of these systems will be broadcasted on blockchain network on run-time and others systems will keep themselves in full synchronization with that information in run-time.
- For both pre-paid and post-paid scenarios, the intrinsic run-time processing capability of blockchain allows telcos to provide to the consumers the visibility on their consumption status for any service they subscriber for ….and this at any time and from anywhere …avoiding consumers billing/credit limit overrides, bill chocks, …etc.
Major improvements (from the traditional systems) are seen as the same information getting updated and synchronized automatically in BSS and registers, eliminating any chance of vulnerability and revenue leakage. So, if BSS has unsubscribed a consumer for getting billed from one particular service, home location register too will unsubscribe that consumer to avail that particular service and vice-versa. The same is processed for a consumer subscription to a service. The major problem of revenue generation or leakage will be solved by the implementation of blockchain as consumers now get billed properly for every service which they are using. This is not only improving service efficiency of telcos but also improves the global customer service experience.
The OSS/BSS segment is expected to hold the highest market size as blockchain would address the concerns in resource inventory management, service assurance, network management, product management, order management, revenue management, and customer management.
12. Blockchain replacing the SIM card?
The SIM card, one of the staples of mobile phones, is facing obsolescence as Blockchain solutions offer significant improvements. With the help of new concepts like blockchain, the smartphones of tomorrow may look familiar, but their technology will be a massive leap forward that’s been a long time coming.
While other hardware-based storage tools upgraded to digital technology—much like video games went from cartridges to digital downloads—SIM technology remains essentially the same as it did when it was created. Now, its dominance is being challenged by eSIM technology, which was first deployed by Google. With blockchain’s help, it’s set to hit the wider market and to make a larger splash.
Blockchain-enabled citizen is uniquely and securely identified anywhere in the world, and use IDs to subscribe to Telco services. He can pick a voice plan from CSP-X, a data plan from CSP-Y and video streaming from CSP-Z and so on. Complete freedom of choice to choose the CSP bundles and offers on a single eSIM ID (compared to the cumbersome multiple SIM cards scenario of traditional systems). And this, for any duration (one-off prepaid package, hourly/daily/monthly subscription, etc.). The eSig set-up/provisioning and blockchain technology will offer the options (various services, bundles, etc.) from any/multiple CSPs of User choice/location…. a significant revenue stream that still creates substantial profits for CSPs.
The Taiwanese firm HTC announced the World’s First Blockchain Smartphone known as Exodus. By being a blockchain technology device, this phone will be the first to have decentralized applications and security (July 2018). Blockchain technology should ensure extra security due to high-level encryption tools, as well as the ability to connect to superfast networks to ensure speedy transactions.
Conclusions
Given the importance of the trillion-dollar industry and its control under the hand of a few, makes the disruption of distributed blockchain technology a need of the day.
Blockchain is currently leading the way in telecom innovation and is changing the economic social landscape of digital communications worldwide. It accommodates telcos biggest need to make their service offerings elastic according to market changing demands.
Blockchain technology can resolve the telcos high pressure to cut down the cost, to enable new revenues streams, service efficiencies, and also keep a check on fraudulent practices while allowing a superior customer experience. It eliminates the traditional complex and long chain of inter-related operations that work jointly to deliver services to customers.
Being a decentralized technology, blockchain completely eliminates the role of expensive infrastructure as well as the need for central authorities or intermediaries. It increases the speed and efficiency of the digital exchange of data between people, departments and provides quicker, efficient and seamless transmission of information.
Blockchain looks instrumental in enabling interoperability between internal as well as external systems for telecom companies. This can bring down infrastructure as well as compliance. Blockchain has the potential to disrupt business models by increasing transparency and effectiveness in the telecom network and its processing. Blockchain decentralized ledger documents fully each transaction that occurs across a distributed or peer-to-peer network, either public, private or hybrid.
In addition, blockchain (recognized as a trusted technology) plays an important role in many areas that conventional systems are technically limited to resolve, such as Service convergence, Real-time transactions, Industry integration,
Usage of 5G capabilities, Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Machine-to-Machine (M2M), Issues related to overabundance of contents, Data traffic explosion, Mobility, Security and many more… where devices connected to the internet automatically orchestrate their interactions
The usage of blockchain based-applications by the telecommunications industry is gaining momentum and eventually will become the norm. The clock is ticking.
The post Blockchain technology in the telecom industry: Part 3 (Reader Forum) appeared first on RCR Wireless News.
