The confluence of 5G and augmented reality has been a cornerstone of digital disruption conversations for quite a while. However, only recently has both 5G and AR/VR been at a level of maturity to truly cooperate and enable new experiences not possible before. Huawei’s recent Better World Summit highlighted this market trend well, with several vendors across AR/VR, networks, and content showcasing both what is happening today and what’s possible going forward.
The forecasted growth rate for the augmented and virtual reality markets is significant, but some objective truths support this growth path.
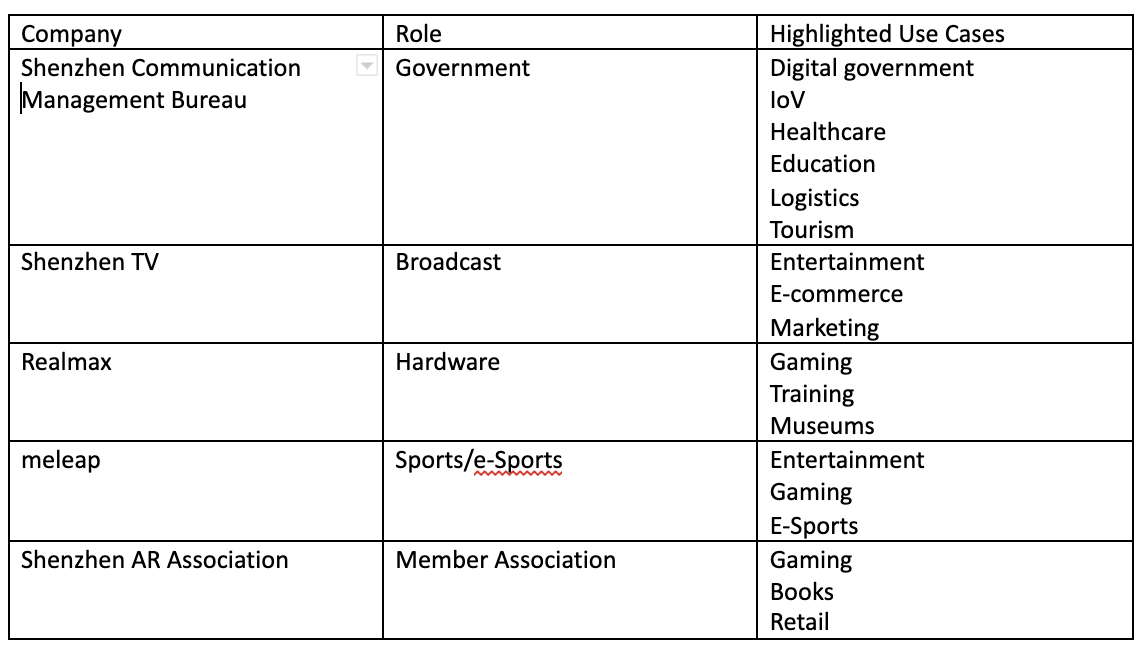
5G is reaching maturity quickly in many regions with operators looking for ways to differentiate their offerings and showcase capability. AR present a very compelling opportunity to do so, with elements like edge streaming/compute and AR cloud stressing not only network bandwidth but also uniformity, latency, and overall reliability. There are 1.5 billion AR enabled devices today (across smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses), and that is before the consumer AR smart glasses market has even begun. Major tech players such as Apple, Google, Samsung, Facebook, Microsoft, and more are at varying stages of AR activity, from strong investment and R&D into full-fledged AR product, software, and services being on the market. Tech giants are not alone either, other players are competing across the value chain. Hardware OEMs like Realwear have been competitive in enterprise, with some early consumer entrants like nReal and Realmax also in the market.
The potential for these companies and devices is broad, pulling in numerous use cases and target verticals where AR can deliver value. Today, this has mostly been in enterprise applications, such as remote worker enablement and training; however, as 5G matures alongside the consumer AR and VR markets, that consumer element combines with enterprise to create ubiquitous opportunity.
Social media, entertainment, education, collaboration, healthcare, and retail are some of the most promising growth areas for AR when leveraging 5G.
The beginnings of social media AR are already in place, with AR filters and advertising on popular social media platforms. Retail is also well-established, with applications like virtual try-on and AR product visualization already being leveraged by brands and retailers.
With COVID-19, the need for immersive collaboration was forced into the spotlight; combined with some of the momentum around broader enterprise digitization, immersive collaboration will continue to grow.
Education and entertainment are both ripe for AR value add but have not yet seen the same activity level as those other verticals and applications. That is changing, however, again as both AR and 5G mature alongside each other to deliver experiences that were not possible in the past.
One of the companies included in the Better World Summit was meleap, creator of an AR sport called Hado; Hado is already in 37 countries with almost 3 million total players; the digital sport is similar to a combination of esports and traditional sports in terms of content and network demands. There is both an audience aspect (like broadcast and/or streaming for sports and esports) as well as the sport itself leveraging the network. Great coverage with low latency can enable multiplayer games with the required connectivity level, true for both tournaments at dedicated locations as well as regular consumers wherever they are.
LG U+ was also included in the Summit, with a focus on opportunities and activity in education. LG U+ partnered with KDDI to enable an AR library for education content. This has expanded into a broader education platform with content subscriptions and content sourced from several areas; an effort from KT is targeting teaches and online classes as well.
Enabling technologies and cross-market support fulfill the 5G and AR potential
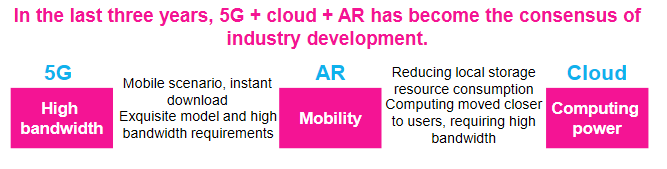
To fully realize the potential of the 5G and AR markets together, of course both 5G and AR must work together, but other technologies like AI/ML and machine vision, edge compute, IoT, and smart city systems also need to be mature and properly integrated into various ecosystems.
Network benefits in latency and total bandwidth are the easiest to understand. Offloading processing from the device to the network will allow for better battery life and smaller form factor devices, but this requires low latency and high quality of service to deliver a good user experience. Existing connectivity methods often fall short in one or both areas, whereas 5G can ensure both latency and network quality. In mission critical applications, network slicing can even be used for guaranteed quality of service for specific applications.
Positioning is another element of the network that will benefit immersive content. 5G positioning can be more accurate than GPS, which is required for accuracy sensitive AR/VR tracking. Also, 5G positioning works indoors; compared to GPS or other indoor positioning technologies, 5G again has the advantage.
Outside of the network, other enabling technologies help enable this aggressive 5G and AR vision. For instance, AI is a required element for machine vision, and improving machine vision speed and accuracy improves user experience. With 5G, some of this processing that has so far been on device can be offloaded to the network, leveraging 5G’s low latency to maintain that user experience. Products such as Apple ARKit, PTC Vuforia, and Huawei’s AR Engine leverage AI to enable multiple tracking types—broad motion, environment, face, hand, gestures, etc.
AR’s far-reaching applicability also means technologies not necessarily required for AR can be leveraged for some use cases. For instance, as immersive device usage becomes more ubiquitous, the need for content to match that breadth grows. In the home, this is easy to deliver on, but in public and on the move use cases, it is a different story. IoT is already being leveraged in the enterprise as a data source for AR usage. In a similar way, V2X communication and smart city connectivity can be used to empower immersive experiences with data as well.
Conclusions
Huawei has been prolific in its messaging around the capabilities of 5G and AR/VR for years, and that continues to be the case with this summit. Globally, other vendors and partnerships are forming as well, positioning 5G and its enablers as a key facet of the augmented and virtual reality market going forward. The summit showed off a broad selection of operators and use cases, which highlights the wide applicability and value of 5G. Network operators have an opportunity to prove capability and value for AR/VR use cases, and the AR/VR market will continue to look for enabling technologies like 5G, AI, and edge compute to enhance solutions and experiences.
Overall, it is exciting to see enabling technologies mesh together in an impactful way. For years, 5G and AR have been paired together as important technology partners, and today we are seeing that partnership grow. AR devices are maturing and becoming more numerous, and content is following both in quality and quantity. 5G’s strengths in latency and total throughput support some of the most promising AR use cases, and other elements like positioning and network slicing will expand that support even further. Operators recognize the opportunities both as a partner and AR/VR use case enabler. All these elements together create a compelling and receptive market that will enable the significant growth expected in AR/VR across both enterprise and consumer segments.
The post 5G and augmented reality becoming a reality (Analyst Angle) appeared first on RCR Wireless News.
