Network function (NF) placement, or homing, is a set of smart algorithms which deploy services automatically across multiple sites and multiple clouds, based on a wide variety of intent and policy constraints including capacity, location, platform capabilities and other service specific parameters.
Optimization of NF placement in a dynamically-changing environment like a mobile network is a challenge. In the 5G era, the need to guarantee QoS for slice-based services makes this even more complex. Networks are becoming virtual and cloud based, and there is a need to manage this new agility and complexity.
Of course, operators are doing NF placement, today. However, with the advent of 5G, new use cases based on network slicing will require committed SLAs around attributes like latency and capacity. To guarantee these SLAs for mobile and nomadic users, operators will need to move from the existing static NF placement to dynamic and real-time NF placement in order to manage network resources that can be scaled up and down to meet the needs of nomadic and mobile users.
The resource duplication workarounds of existing NF placement will become increasingly inefficient and costly as 5G networks evolve and network slicing enables an ever-increasing array of differentiated, QoS-based services. Dynamic NF placement has a critical role to play in these services. As an example, in a disaster situation, ensuring SLAs for first-responder communications is vital. To achieve this the orchestration system needs to dynamically utilize telco cloud, public cloud and edge resources to meet mobile, high priority, unpredictable and rapidly changing demands.
As service providers build out their 5G core and populate the RAN with 5G new radio in preparation for the next generation of differentiated services that will drive 5G monetization, it is vital that they build an intelligent, intent-based NF placement solution that is smart enough to translate the business inputs that define a differentiated service into the underlying parameters for the orchestration system. And the orchestration system will need to step up too. Required capabilities include multi-vendor end-to-end orchestration across the RAN, transport and core domains that is adaptive in real-time, business-intent and network topology aware (aware of geographic locations such as edge locations), and service, application and slice aware.
The goal is fully autonomous NF placement but that won’t happen overnight. Recent research by AvidThink proposes the following pragmatic, phased approach.
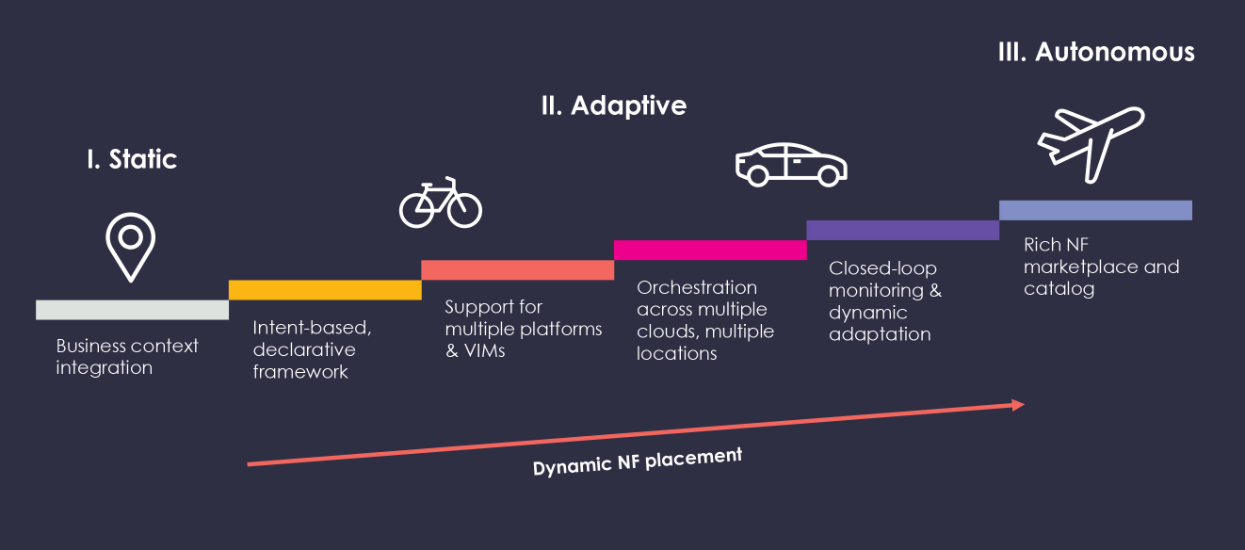
Fig. 1 – Three stages on the road to autonomous NF placement
Phase 1 – Static: Pre-instantiated NF placement based on peak-hour traffic planning, relying on resource duplication as a workaround to ensure sufficient resources exist where they might be needed.
Phase 2 – Adaptive: Optimized, multi-site, intent- and policy-based NF placement in a closed-loop environment.
Phase 3 – Autonomous: Dynamic orchestration and re-allocation of network functions based on AI/ML inputs.
This phased approach starts by addressing today’s realities and builds towards autonomous NF placement to meet the demands of tomorrow’s evolving 5G slice-based possibilities.
To learn more about dynamic NF placement and its critical role in successful 5G deployments read AvidThink’s report.
The post Dynamic network function placement is essential in the 5G era appeared first on RCR Wireless News.
